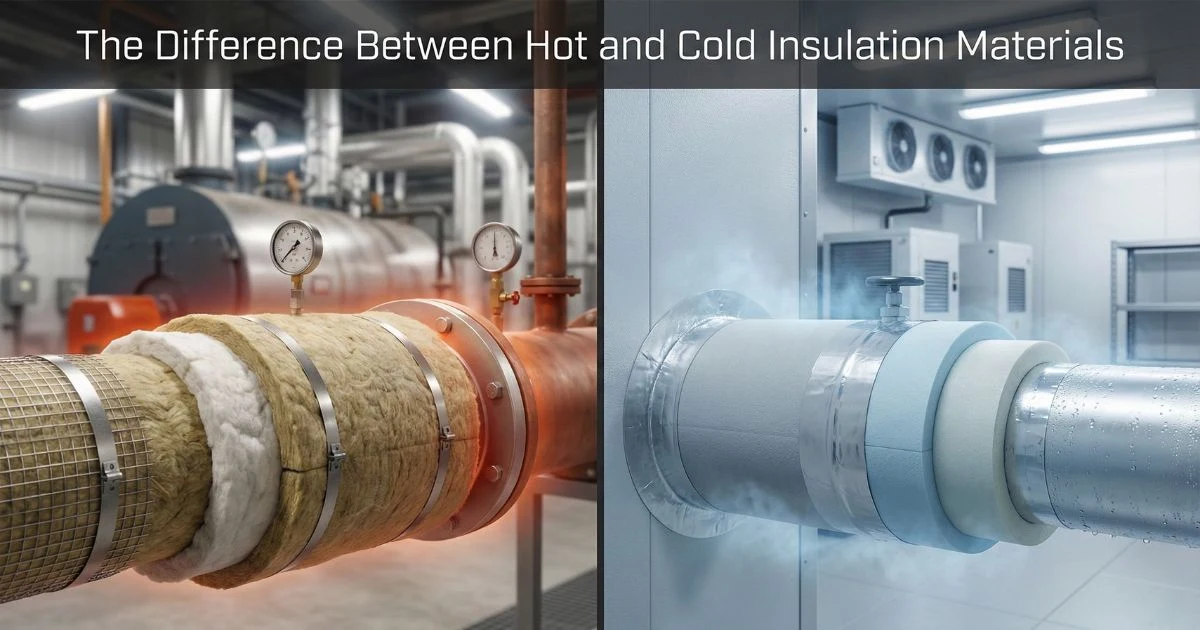
When people search for the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials, they usually want one simple answer: which one do I need? But the real answer goes deeper. The right insulation does more than control temperature. It protects equipment, saves energy, reduces costs, improves safety, and supports sustainability goals. At Amit Insulation, we’ve seen how choosing the wrong insulation can increase energy bills, cause condensation damage, and even shorten equipment life. That’s why understanding the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials is not just technical knowledge—it’s a smart business decision.
What Is Insulation and Why It Matters
Insulation is a protective layer that reduces heat transfer. Heat always moves from a hotter area to a colder area. Insulation slows that movement. That’s it. Simple. But its impact? Huge.
Without insulation:
- Steam pipes lose heat.
- Chillers sweat and drip.
- Energy bills increase.
- Equipment fails faster.
According to 2026 industrial energy reports, nearly 18–22% of industrial heat loss happens due to poor or damaged insulation. That’s money literally disappearing into the air.
Understanding the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials helps you:
- Reduce operational costs
- Improve safety
- Prevent corrosion
- Increase system lifespan
In short, insulation is not an expense. It’s an investment.
Why the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials Is Important
Many people assume insulation is just insulation. But the difference between hot and cold insulation is critical. If you use hot insulation material on a cold system:
- Condensation will form.
- Moisture will penetrate.
- Corrosion under insulation (CUI) will start.
If you use cold insulation on high-temperature pipes:
- The material may degrade.
- Fire risks increase.
- Efficiency drops.
That’s why knowing the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials protects your equipment and your budget. In 2026, with stricter environmental regulations and rising energy costs, industries cannot afford insulation mistakes.
What Is Hot Insulation?
Hot insulation is designed to prevent heat loss from high-temperature systems. It keeps thermal energy inside pipes, boilers, reactors, and furnaces. Think of it like a thermos bottle—it keeps heat trapped inside.
Common Temperature Range:
Above ambient temperature, often up to 600°C or more.
Main Goals:
- Reduce heat loss
- Improve energy efficiency
- Protect workers from burns
- Maintain process temperature
Typical Applications:
- Steam pipelines
- Thermal power plants
- Oil refineries
- Chemical plants
The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials becomes clear here. Hot insulation focuses on retaining heat and ensuring system efficiency.
What Is Cold Insulation?
Cold insulation works in the opposite direction. It prevents external heat from entering cold systems. Imagine a refrigerator. If warm air keeps entering, cooling efficiency drops. That’s where cold insulation comes in.
Common Temperature Range:
Below ambient temperature, sometimes as low as -50°C.
Main Goals:
- Prevent condensation
- Stop energy loss
- Avoid moisture damage
- Protect system integrity
Common Applications:
- HVAC systems
- Chilled water lines
- Cold storage facilities
- Pharmaceutical plants
The difference between hot insulation and cold insulation Materials is especially noticeable in moisture control. Cold insulation always requires vapor barriers.
Core Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials
Let’s simplify the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials:
| Feature | Hot Insulation | Cold Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Keeps heat inside | Keeps heat outside |
| Main Risk | Heat loss | Condensation |
| Vapor Barrier | Optional | Mandatory |
| Fire Resistance | Very important | Moderate |
| Temperature Direction | High temp systems | Low temp systems |
The difference between hot insulation and cold insulation mainly depends on temperature direction and moisture management.
Hot insulation = stop heat from escaping.
Cold insulation = stop heat and moisture from entering.
Materials Used in Hot Insulation
Selecting materials defines performance. Common hot insulation materials include:
- Rock wool
- Ceramic fiber
- Calcium silicate
- Glass wool
Comparison Table
| Material | Max Temp | Fire Resistance | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rock Wool | 750°C | Excellent | High |
| Ceramic Fiber | 1260°C | Superior | Medium |
| Calcium Silicate | 650°C | Excellent | Very High |
| Glass Wool | 450°C | Good | Medium |
These materials are engineered to withstand extreme heat. That’s a key part of the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials.
Materials Used in Cold Insulation
Cold insulation materials focus on low thermal conductivity and moisture resistance. Common materials:
- Polyurethane Foam (PUF)
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
- Nitrile Rubber
Why Closed-Cell Structure Matters
Closed-cell materials prevent water penetration. Without it, insulation performance drops quickly. The difference between hot insulation and cold insulation Materials becomes obvious here—moisture control is non-negotiable in cold systems.
Industrial Applications and Real-World Use
Industries rarely use just one type. Most use both.
Example: A refinery uses:
- Hot insulation for steam lines
- Cold insulation for refrigeration units
Understanding the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials ensures each system performs optimally. If you’re exploring Hot & Cold Insulation in Gujarat, choosing an experienced provider like Amit Insulation ensures technical accuracy and long-term reliability. You can also explore insights like How Heat Insulation Sheets Help in Summers to understand how seasonal temperature control impacts cost savings. The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials plays a central role in meeting sustainability goals.
Installation Differences Explained
Even the best material fails if installed poorly.
Hot Insulation Installation:
- Maintain uniform thickness
- Secure joints tightly
- Ensure mechanical protection
Cold Insulation Installation:
- Seal every joint
- Install vapor barriers properly
- Avoid air gaps
Improper installation can reduce insulation performance by 20–25%.
The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials directly affects installation techniques.
Cost Comparison Table
| Factor | Hot Insulation | Cold Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
| Lifespan | 15–20 years | 10–15 years |
| Energy Savings | High | Very High |
Cold insulation may cost more initially but often results in higher energy savings in cooling systems.
Maintenance & Inspection Guidelines
Inspection should be done every 6–12 months. Check for:
- Moisture intrusion
- Cracks or gaps
- Surface damage
- Corrosion
The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials also affects inspection frequency—cold insulation requires closer moisture monitoring.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these errors:
- Ignoring vapor barriers
- Using incorrect material thickness
- Mixing hot and cold materials
- Delaying maintenance
- Choosing low-quality suppliers
Working with experts like Amit Insulation eliminates these risks.
How to Choose the Right Insulation System
Ask yourself:
- What is the operating temperature?
- Is condensation possible?
- What is the humidity level?
- What safety standards apply?
- What is your long-term energy goal?
The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials should guide your decision. For facilities needing soundproofing as well, solutions like Acoustic Insulation Solutions Manufacturer & Supplier in Vadodara can complement thermal insulation.
Why Businesses Trust Amit Insulation
At Amit Insulation, we specialize in identifying the exact Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials for your project.
We provide:
- Site inspection
- Custom insulation design
- Energy audits
- Professional installation
- Long-term maintenance
Our solutions align with 2026 efficiency and sustainability standards. When insulation is done right, savings multiply.
Conclusion
The Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials is simple in theory but powerful in impact. Hot insulation keeps heat inside. Cold insulation keeps heat and moisture outside. Understanding the difference between hot insulation and cold insulation Materials helps prevent costly mistakes, reduce energy waste, and protect infrastructure. If you want expert guidance, professional installation, and long-term performance, contact Amit Insulation today. The right insulation today means lower costs tomorrow.
FAQs
1. What is the Difference Between Hot and Cold Insulation Materials?
Hot insulation prevents heat loss, while cold insulation prevents heat gain and condensation.
2. Why is vapor barrier important in cold insulation?
It prevents moisture buildup, which can cause corrosion and system damage.
3. Which insulation saves more energy?
Both are efficient, but cold insulation often shows higher visible savings in cooling systems.
4. How often should insulation be inspected?
Every 6–12 months for optimal performance.
5. Can one material be used for both systems?
Generally no. The difference between hot insulation and cold insulation requires specific properties.